Instrument
X-ray Diffractometer (XRD)
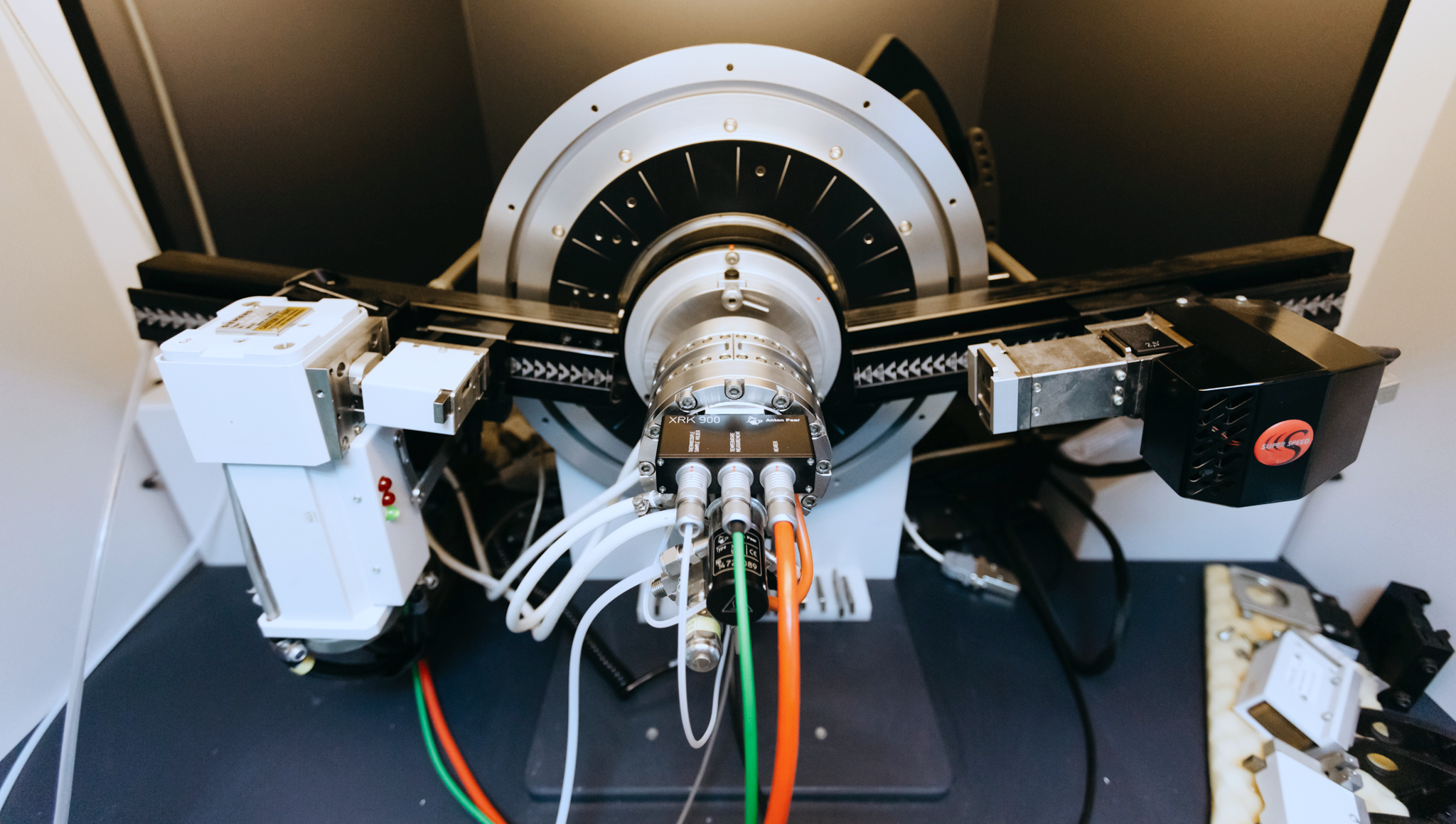
X-Ray Diffraction is a well-known technique for the investigation of the structure of crystalline solids and powders. X-rays wavelength is between the ultraviolet and gamma rays in the electromagnetic spectrum, and its magnitude is of the same order of interatomic distances in crystals. Depending on the x-ray wavelength, crystal orientation and structure, a beam of X-rays falling on a crystal undergoes diffraction. The x-ray beam interacts with the electron density of atoms or ions of the crystal lattice, thus producing a specific electron map for the crystalline material investigated. Each crystal has a unique pattern and X-Ray diffraction gives a fingerprint of the studied material. The data collected from the reflections at various angles are analysed according to Bragg’ s law. Powder X-ray Diffraction is widely used both for the qualitative analysis of crystalline materials and for the quantitative measurements of crystalline components in composite materials.
Characteristics
X-Ray Diffraction is a well-known technique for the investigation of the structure of crystalline solids and powders. X-rays wavelength is between the ultraviolet and gamma rays in the electromagnetic spectrum, and its magnitude is of the same order of interatomic distances in crystals. Depending on the x-ray wavelength, crystal orientation and structure, a beam of X-rays falling on a crystal undergoes diffraction. The x-ray beam interacts with the electron density of atoms or ions of the crystal lattice, thus producing a specific electron map for the crystalline material investigated. Each crystal has a unique pattern and X-Ray diffraction gives a fingerprint of the studied material. The data collected from the reflections at various angles are analysed according to Bragg’ s law. Powder X-ray Diffraction is widely used both for the qualitative analysis of crystalline materials and for the quantitative measurements of crystalline components in composite materials.
Services
Bruker D8 Advance
CuKa radiation, Bragg-Brentano geometry (2θ:0-1600)
1D & 0D detectors
Parallel beam optics, Knife edge collimators, Soller slits
Diffracted beam monochromator
Thin Film attachment
High-temperature furnace (300-1173K)
Appropriate software for instrument control and analysis
Sample Properties
Powders, pellets, solids, films
Sample size: 20mm dia
Weight: some mg



